Knee osteoarthritis (Knee-OA) is a debilitating bone and joint disease with the potential to necessitate joint replacement. It poses a significant health concern, as it carries a substantial lifetime risk of 45% [1]. This condition affects an enormous population, with over 200 million patients worldwide [2]. Furthermore, the high prevalence of knee X-rays in the European Union in 2020, totaling approximately 100 million [3], underscores the urgent need for effective strategies to manage and treat Knee-OA.
KOALA™ enhances physician agreement rates, offers precise measurements, and streamlines workflow for more efficient knee X-ray assessments.
87% sensitivity and 83% specificity discerning mild from moderate and severe knee OA based on KL score (>=2) [5]
23% increase in physician’s agreement rate to gold standard [6]
Workflow time savings range up to 25 days per year
Knee-OA has a lifetime risk of 45%
Over 200M knee-OA patients worldwide
The annual cost per patient ranges up to €10k
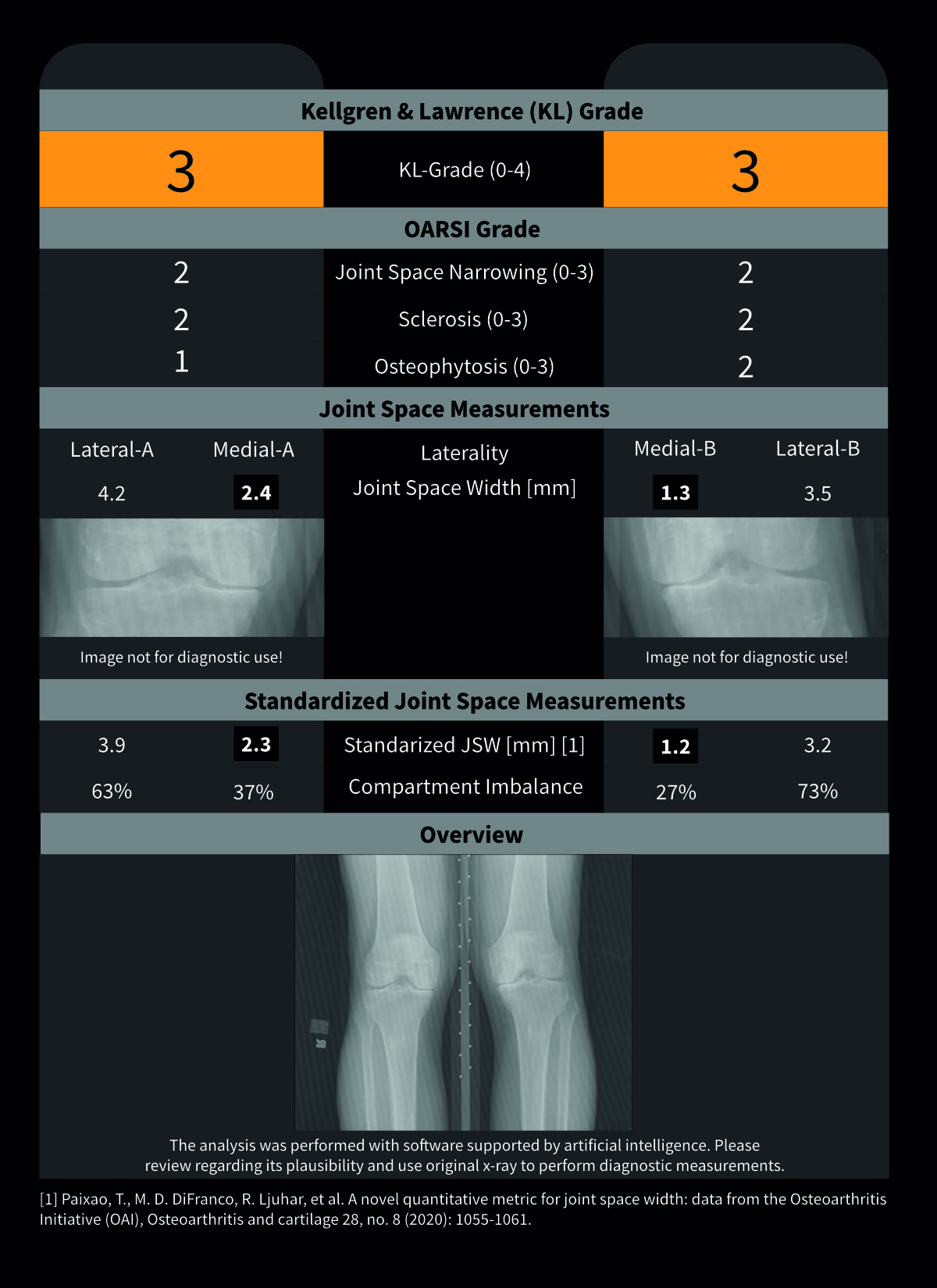
KOALA™ supports physicians in detecting signs of knee osteoarthritis based on standard joint parameters and OARSI criteria of standing radiographs of the knee.
Enables instant, verifiable decision making in difficult cases
Facilitates monitoring of knee osteoarthritis progression
Enhances diagnosing and reporting knee osteoarthritis according to the latest clinical guidelines
IB Lab KOALA is a radiological fully-automated image processing software device intended to aid medical
professionals in the measurement of minimum joint space width; an assessment of the severity of sclerosis,joint space narrowing, and osteophytes based OARSI criteria for these parameters; and, the severity of radiographic knee OA based on Kellgren & Lawrence Grading of standing, fixed-flexion radiographs of the knee. It should not be used in-lieu of full patient evaluation or solely relied upon to make or confirm a diagnosis. The system is to be used by trained professionals including, but not limited to, radiologists, orthopedics, physicians and medical technicians.
[1] Murphy L, Schwartz TA, Helmick CG, Renner JB, Tudor G, Koch G, Dragomir A, Kalsbeek WD, Luta G, Jordan JM. Lifetime risk of symptomatic knee osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2008 Sep 15;59(9):1207-13. doi: 10.1002/art.24021. PMID: 18759314; PMCID: PMC4516049.
[2] GBD 2015 Disease and Injury Incidence and Prevalence Collaborators. Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 310 diseases and injuries, 1990-2015: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. Lancet. 2016 Oct 8;388(10053):1545-1602. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)31678-6. Erratum in: Lancet. 2017 Jan 7;389(10064):e1. PMID: 27733282; PMCID: PMC5055577.
[3] Based on IB Lab Market Study
[4] OA PREVALENCE AND BURDEN
[6] Nehrer, S., Ljuhar, R., Steindl, P., Simon, R., Maurer, D., Ljuhar, D., ... & Paixao, T. (2019). Automated Knee Osteoarthritis Assessment Increases Physicians’ Agreement Rate and Accuracy: Data from the Osteoarthritis Initiative. Cartilage, 1947603519888793.